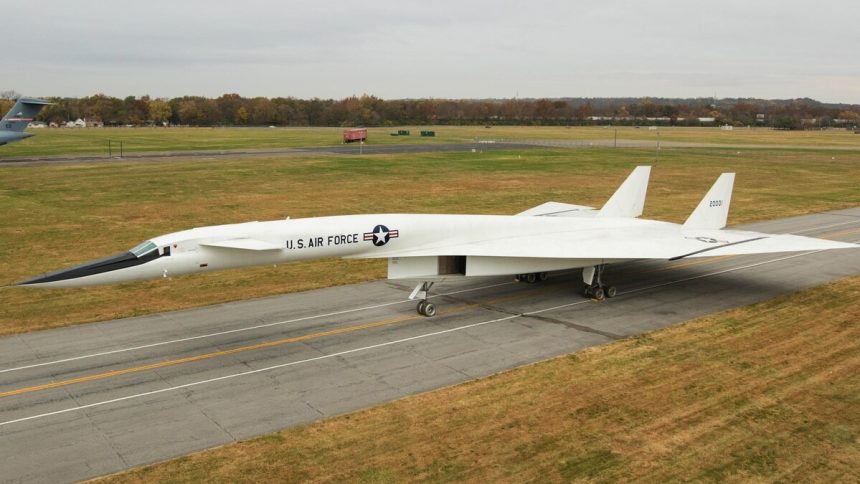
The experimental legacy of the iconic XB-70 Valkyrie, which made its first flight on Sept. 21, 1964.
An article published on the U.S. Air Force website commemorates the 60th anniversary of the first flight of the legendary XB-70 Valkyrie, a supersonic bomber that captured the imagination of aviation enthusiasts and engineers alike. Known for its sleek and futuristic design, the XB-70 remains a symbol of the experimental and ambitious spirit of Cold War-era aircraft development. Despite only two prototypes ever being built, the aircraft has left an indelible mark on military aviation history.
The XB-70 Valkyrie was originally conceived in the 1950s as a high-speed, high-altitude bomber for the U.S. Air Force Strategic Air Command. At a time when technological advancements were rapidly accelerating, the U.S. Air Force sought a bomber capable of flying faster and higher than the B-52 Stratofortress, its workhorse of the era (as well as the backbone of the strategic bomber fleet today and for some more decades in the future…).
With a planned cruise speed of Mach 3 and an operating altitude of 70,000 feet, the XB-70 promised to outpace and outmaneuver Soviet defenses, which were a growing concern during the Cold War.
One of the most remarkable features of the XB-70 was its ability to “ride” its own shockwave, a design innovation that allowed it to maintain stability and performance at supersonic speeds. The Valkyrie’s iconic delta wing, combined with six powerful jet engines, gave it an exotic and striking appearance, making it one of the most visually distinctive aircraft ever built. Its outer wing panels were hinged, allowing them to be lowered during flight to optimize the aerodynamic performance at high speeds.

The article highlights the crucial role played by Arnold Engineering Development Complex (AEDC) in the development of the XB-70.
The testing of the Valkyrie’s engines, aerodynamics, and other key components began at Arnold Air Force Base in the late 1950s, well before the first prototype took shape. The AEDC’s facilities were instrumental in pushing the boundaries of what was possible in aviation at the time. One of the earliest tests involved the air-breathing engine nozzles proposed for the XB-70 in March 1958. This was followed by extensive wind tunnel testing of scale models of the Valkyrie, where the aerodynamic characteristics of bombs dropped from the aircraft were also studied.
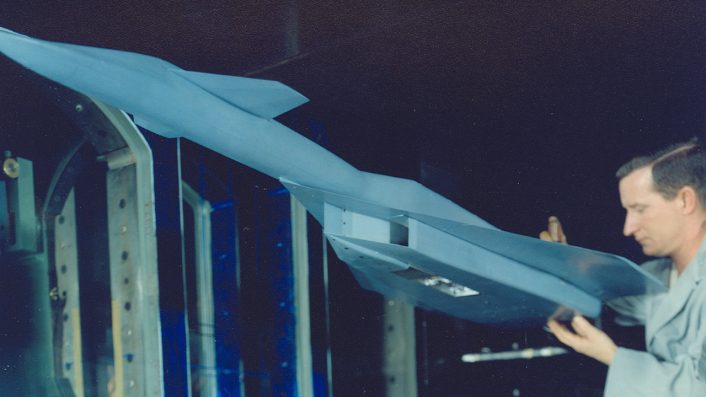
Development continued into the early 1960s, with the YJ93 turbojet engines, designed specifically for the XB-70, undergoing rigorous testing at AEDC. These engines were critical to the Valkyrie’s ability to reach and maintain supersonic speeds. However, in 1961, before the first prototype was even completed, the bomber program was canceled due to budget constraints and concerns over the bomber’s vulnerability to Soviet surface-to-air missiles, which had rapidly advanced in capability.
Although the XB-70 bomber program was terminated, the Valkyrie found new life as a research aircraft.

The U.S. Air Force recognized the potential of the aircraft to serve in aerodynamics and propulsion research, particularly in the study of large supersonic aircraft. Consequently, two XB-70 prototypes were completed, and testing continued, including at AEDC, where a scale version of the XB-70 inlet, paired with a full-scale YJ93 engine, was tested in August 1962.
XB-70A number 1 (62-001) made its first flight from Palmdale to Edwards Air Force Base, CA, on Sept. 21, 1964. The second XB-70A (62-207) made its first flight on Jul. 17, 1965. The latter differed from the first prototype for being built with an added 5 degrees of dihedral on the wings as suggested by the NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA, wind-tunnel studies.

While the 62-001 made only one flight above Mach 3, because of poor directional stability experienced past Mach 2.5, the second XB-70, achieved Mach 3 for the first time on Jan. 3, 1966 and successfully completed a total of nine Mach 3 flights by June on the same year.
However, the Valkyrie program suffered a devastating setback in June 1966 when the second prototype was destroyed in a midair collision with an F-104N Starfighter during a photoshoot. This tragic accident resulted in the loss of key personnel and diminished the future prospects of the Valkyrie.
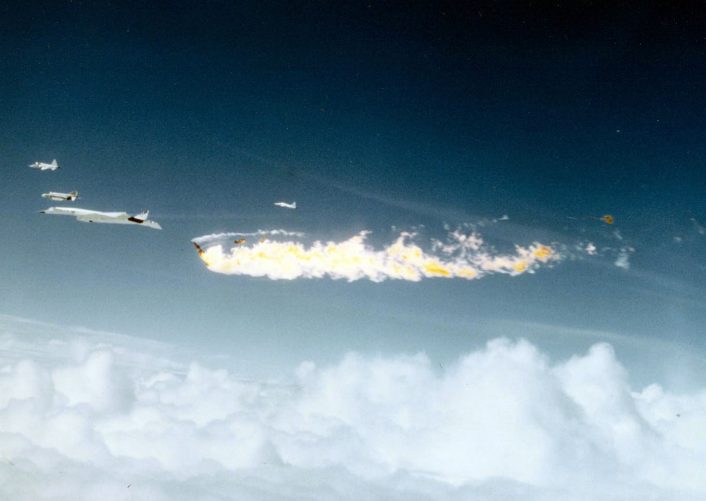

Despite this setback, the remaining XB-70 continued to serve as a valuable research platform. In 1967, the U.S. Air Force transferred the aircraft to NASA, where it was used in support of the National Supersonic Transport (SST) program. NASA employed the XB-70 to investigate supersonic flight operations, but the SST program was eventually canceled in 1971, marking the end of America’s efforts to develop a commercial supersonic airliner.
The XB-70 Valkyrie’s final flight took place on Feb. 4, 1969, when it was flown to Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Ohio. There, the aircraft was placed on display at what is now the National Museum of the United States Air Force, where it remains a testament to the audacious engineering and design of its era.
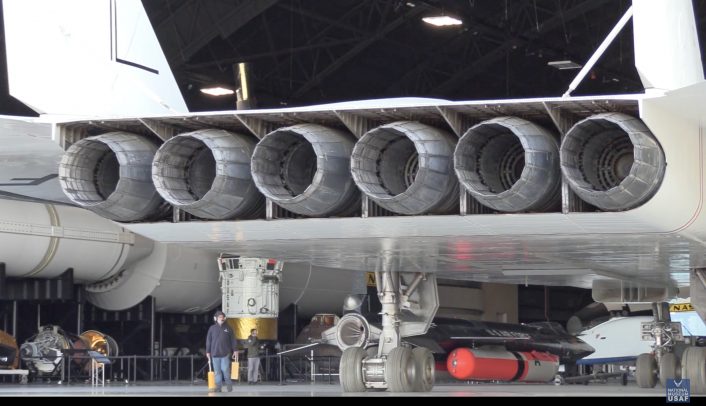

Though only two XB-70s were ever built, their legacy endures: the aircraft’s pioneering advancements in aerodynamics, engine performance, and high-speed flight helped shape the future of supersonic aviation.

The first prototype made a total of 83 flights, amassing 160 hours and 16 minutes of flight time, while the second prototype completed 46 flights, totaling 92 hours and 22 minutes.
The XB-70 Valkyrie, with its daring design and groundbreaking capabilities, continues to captivate aviation enthusiasts and engineers. Its story, though short-lived in terms of operational use, highlights the relentless pursuit of innovation that defines the U.S. Air Force and its engineering partners. Sixty years after its first flight, the Valkyrie remains an iconic symbol of the bold ambitions of Cold War-era aviation.










